A Comprehensive Guide to Project-Based Lesson Planning for Teachers
Project-based lesson planning Guide
Introduction to Project-Based Learning (PBL)
Project-Based Learning (PBL) is an instructional approach where students gain knowledge and skills by working on extended projects. These projects address real-world problems and challenges, promoting deep learning and practical application of concepts. PBL encourages students to explore, create, and collaborate, making learning more engaging and meaningful.
Benefits of Project-Based Learning
- Enhanced Engagement: Students are more motivated when learning through projects that interest them.
- Development of Critical Skills: PBL fosters problem-solving, critical thinking, collaboration, and communication skills.
- Real-World Application: Students apply what they learn in class to real-world situations, making education relevant.
- Independent Learning: Encourages self-directed learning and responsibility.
Steps to Planning a Project-Based Lesson
-
Identify Learning Objectives:
- Determine the key concepts and skills you want students to learn.
- Align these objectives with curriculum standards and student interests.
-
Choose a Real-World Problem or Question:
- Select a problem or question that is relevant and challenging.
- Ensure it requires critical thinking and creativity to solve.
-
Plan the Project Scope:
- Define the project's duration and major milestones.
- Break down the project into manageable tasks and phases.
-
Design the Project Outline:
- Create a detailed plan that includes the project's goals, timeline, resources, and assessment criteria.
- Outline the roles and responsibilities of students.
-
Develop Assessments:
- Design formative and summative assessments to evaluate student learning.
- Include self-assessment and peer assessment opportunities.
-
Gather Resources:
- Identify and gather materials, tools, and resources needed for the project.
- Arrange access to technology, experts, and community resources if necessary.
-
Create a Flexible Schedule:
- Develop a timeline with flexible deadlines to accommodate different learning paces.
- Include regular check-ins and progress reviews.
-
Facilitate and Guide:
- Act as a facilitator, guiding students through the project.
- Provide support, feedback, and resources as needed.
-
Encourage Collaboration:
- Promote teamwork and collaboration among students.
- Use group activities, discussions, and peer reviews to foster a collaborative environment.
-
Reflect and Evaluate:
- Allow time for reflection on what was learned and how the project was conducted.
- Use reflections to improve future projects.
Example Project-Based Lesson Plan:
Topic: Environmental Conservation
Grade Level: 7
Duration: 4 weeks
Objective: Students will understand the importance of environmental conservation by researching local environmental issues and proposing actionable solutions.
Project Outline:
-
Week 1: Introduction and Research
- Introduce the project and its goals.
- Discuss local environmental issues.
- Assign research topics to student groups.
-
Week 2: Investigation and Data Collection
- Students gather data and information on their assigned topics.
- Conduct interviews with local experts or community members.
- Document findings in a research journal.
-
Week 3: Solution Development
- Students brainstorm and develop possible solutions to the issues they researched.
- Create presentations or prototypes of their solutions.
-
Week 4: Presentation and Reflection
- Students present their findings and solutions to the class or a panel of community members.
- Reflect on the project, discussing what they learned and how they can apply it in the future.
Assessment:
- Formative: Research journals, progress check-ins, group discussions.
- Summative: Final presentation, peer evaluations, self-reflection essays.
Resources Needed:
- Access to the internet and library resources
- Interview guidelines and contact information for experts
- Materials for creating presentations or prototypes
Tips for Successful Project-Based Learning:
- Start Small: Begin with shorter projects to build students' confidence and skills.
- Be Flexible: Adapt plans as needed to meet student needs and interests.
- Provide Clear Expectations: Clearly communicate project goals, expectations, and assessment criteria.
- Incorporate Technology: Use technology to enhance research, collaboration, and presentations.
- Celebrate Success: Acknowledge and celebrate student achievements and project milestones.
Conclusion
Project-Based Learning is a powerful approach to education that engages students, promotes critical skills, and connects classroom learning to the real world. By carefully planning and facilitating projects, teachers can create dynamic and meaningful learning experiences that inspire and empower students.
References
- Buck Institute for Education (BIE): Comprehensive resources on PBL, including planning guides and project ideas.
- Edutopia: Articles, videos, and case studies on effective PBL practices.
- PBL Works: Tools and resources for planning and implementing project-based learning in the classroom.
Super Admin
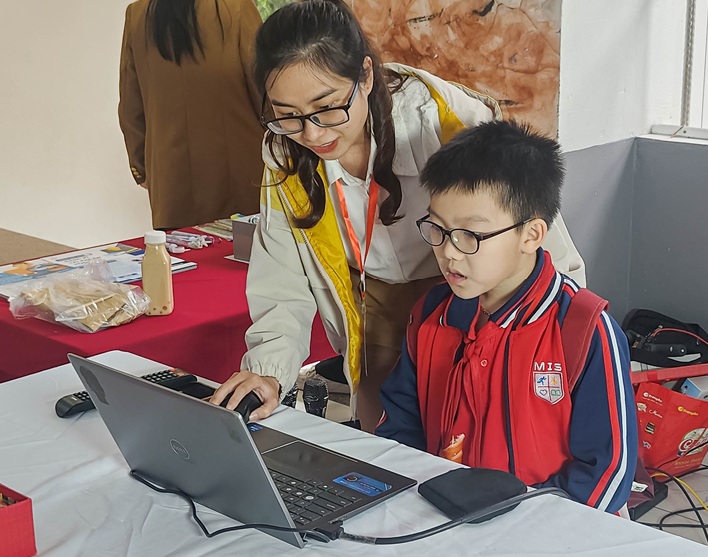

Ademy Vietnam at MIS Innovation Day: Introducing Effective Self-Learning Solutions
On March 29, 2025, Ademy Vietnam participated in the MIS Innovation Day – an event focused on science, technology, and culture, attracting thousands of students and parents from Hanoi and surrounding provinces.

Psychological Methods for Improving Students' Memorization of Lesson Content
Improving Students' Memorization

The Powerful Impact of Video on Teaching and Learning: Insights from Professional Research
Impact of Video on Teaching and Learning

The Importance of Teaching Positive Education Skills
Positive Psychology in Schools
Enhancing Student Memory: Effective Strategies and Techniques
Improving students' memory