Enhancing Student Memory: Effective Strategies and Techniques
Improving students' memory
Introduction
Memory plays a crucial role in the learning process, serving as the foundation upon which knowledge is built and retained. For students, improving memory can lead to better academic performance and a deeper understanding of subject matter. This article explores various methods that educators and students can use to enhance memory retention and recall.
1. Active Learning Techniques
a. Interactive Engagement
- Method: Engage students in active participation through discussions, group activities, and hands-on projects.
- Benefit: Encourages deeper processing of information, making it easier to remember.
b. Teaching Others
- Method: Have students explain concepts to their peers.
- Benefit: Teaching reinforces the material in the student’s mind, leading to better retention.
2. Mnemonic Devices
a. Acronyms and Acrostics
- Method: Create acronyms or acrostics to remember lists or sequences (e.g., PEMDAS for the order of operations in mathematics).
- Benefit: Simplifies complex information into easy-to-recall formats.
b. Visualization and Imagery
- Method: Encourage students to create mental images or mind maps to represent information.
- Benefit: Visual imagery can make abstract concepts more concrete and memorable.
3. Spaced Repetition
a. Review Schedule
- Method: Implement a schedule that involves reviewing material at increasing intervals (e.g., one day after learning, one week later, then one month later).
- Benefit: Reinforces memory through repeated exposure over time, combating forgetting.
b. Flashcards
- Method: Use flashcards for spaced repetition, regularly shuffling and reviewing them.
- Benefit: Promotes active recall and spaced practice, enhancing long-term retention.
4. Organizational Strategies
a. Chunking
- Method: Break down large pieces of information into smaller, manageable chunks (e.g., breaking down a long number into smaller groups).
- Benefit: Reduces cognitive load and makes information easier to process and remember.
b. Categorization
- Method: Organize information into categories or groups.
- Benefit: Helps students see relationships between concepts, improving recall.
5. Enhancing Understanding
a. Connect New Information to Existing Knowledge
- Method: Relate new material to what students already know.
- Benefit: Builds stronger neural connections, making new information easier to remember.
b. Use Multiple Modalities
- Method: Present information using various formats (visual, auditory, kinesthetic).
- Benefit: Engages different parts of the brain, reinforcing memory through multiple pathways.
6. Healthy Lifestyle Habits
a. Adequate Sleep
- Method: Encourage students to get sufficient sleep, particularly after learning new material.
- Benefit: Sleep plays a critical role in memory consolidation, helping to transfer information from short-term to long-term memory.
b. Proper Nutrition
- Method: Promote a balanced diet rich in brain-boosting nutrients (e.g., omega-3 fatty acids, antioxidants).
- Benefit: Supports overall brain health and cognitive function.
c. Regular Physical Activity
- Method: Incorporate physical activities into the daily routine.
- Benefit: Exercise increases blood flow to the brain and has been shown to improve memory and learning.
7. Reducing Cognitive Load
a. Simplifying Instructions
- Method: Break instructions into clear, concise steps.
- Benefit: Reduces the mental effort required to understand and follow instructions, leaving more cognitive resources for learning and memory.
b. Managing Stress
- Method: Teach stress-management techniques such as mindfulness, meditation, or deep breathing exercises.
- Benefit: Reduces anxiety, which can interfere with memory formation and recall.
8. Technological Aids
a. Educational Apps
- Method: Utilize apps designed for memory enhancement, such as those that offer spaced repetition or gamified learning experiences.
- Benefit: Provides interactive and engaging ways to reinforce memory.
b. Online Resources
- Method: Incorporate online quizzes, videos, and interactive tutorials.
- Benefit: Offers diverse ways to present and review information, catering to different learning styles.
Conclusion
Improving student memory is a multifaceted process that involves active learning, mnemonic devices, spaced repetition, organizational strategies, and healthy lifestyle habits. By incorporating these methods into teaching practices, educators can help students enhance their memory retention and recall, leading to improved academic performance and a deeper understanding of the material. Encouraging students to adopt these techniques will not only benefit their immediate learning but also equip them with valuable skills for lifelong learning.
References
- National Institute on Aging: Provides research on brain health and memory.
- Edutopia: Articles on active learning and memory-enhancing strategies.
- Learning Scientists: Resources and research on effective study techniques and memory improvement strategies.
Super Admin
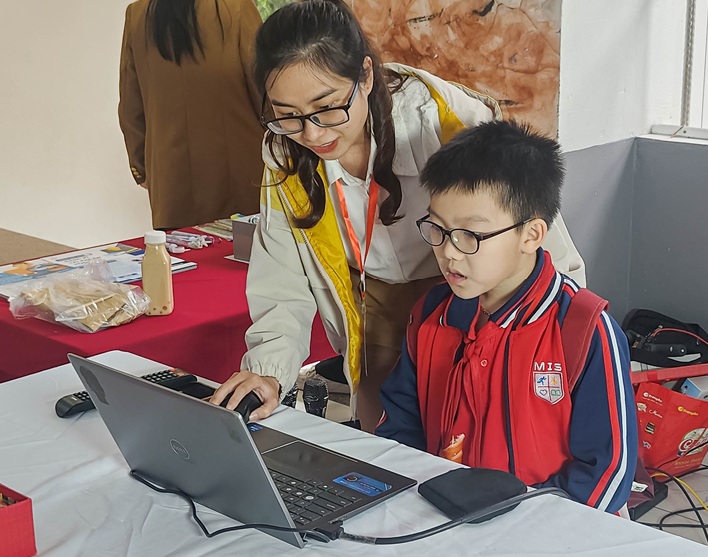

Ademy Vietnam at MIS Innovation Day: Introducing Effective Self-Learning Solutions
On March 29, 2025, Ademy Vietnam participated in the MIS Innovation Day – an event focused on science, technology, and culture, attracting thousands of students and parents from Hanoi and surrounding provinces.

Psychological Methods for Improving Students' Memorization of Lesson Content
Improving Students' Memorization

The Powerful Impact of Video on Teaching and Learning: Insights from Professional Research
Impact of Video on Teaching and Learning

The Importance of Teaching Positive Education Skills
Positive Psychology in Schools
A Comprehensive Guide to Flipped-Classroom Lesson Planning for Secondary Teachers
Flipped-classroom lesson planning guide